Green Compliance in Plastics Manufacturing: CSRD in 2024
As of 1 January 2024, plastics manufacturers face requirements of transparency, accountability, and sustainable practices as mandated by the CSRD.
This article will guide you through the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive and its implications for the plastics manufacturing industry. We will present the regulations and key provisions of the CSRD and explore how these changes will redefine the future of plastics manufacturing for a more sustainable and circular economy.

Understanding the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
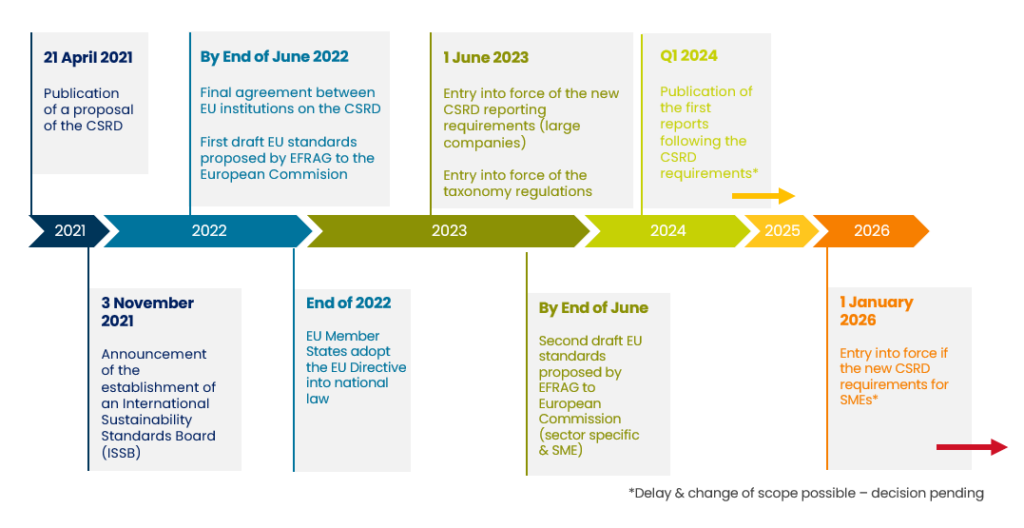
Having come into force in January 2023, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, introduced by the European Union, is a pivotal directive within the context of the EU Green Deal. The CSRD is a successor to the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD), described further. The CSRD furthers corporate reporting by enhancing disclosure requirements and pushing companies to disclose a more comprehensive set of non-financial information.
Key Objectives of the CSRD
The CSRD aims to increase transparency, accountability, and sustainability. Its objective is to bridge the information gap between companies and stakeholders, ensuring that environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are measured and disclosed. The directive seeks to create a standardized reporting framework for better business comparability and enables investors, consumers, and policymakers to make informed decisions that align with sustainability goals.
From NFRD to CSRD
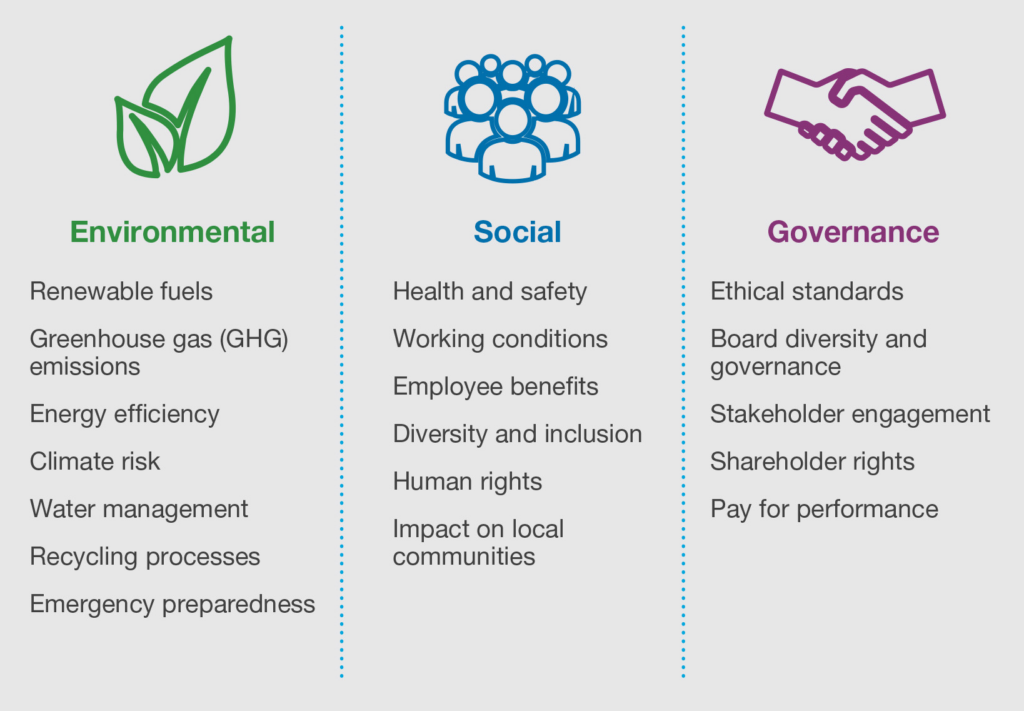
While the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) had applied to large public-interest entities, the CSRD expands its scope to include a broader spectrum of companies, including listed companies and certain large non-listed entities.
Additionally, the NFRD had more flexible reporting requirements, while the CSRD introduced mandatory sustainability reporting on both financial and non-financial aspects for all large companies. Further, with the CSRD, companies must disclose information on their business model, policies, and due diligence processes concerning environmental, social, and governance matters.
The information to be disclosed according to the CSRD includes but is not limited to climate change impact, resource usage, human rights considerations, and diversity policies.
Critical Changes for Plastics Manufacturers Starting 1 January 2024
In this section, we will explore the specific changes that will come into effect on 1 January 2024 for companies already covered by the CSRD and discuss how these changes will impact the day-to-day operations and reporting practices of companies in the plastics industry.
Comprehensive Sustainability Indicators
Plastics manufacturers will be required to provide detailed information on various sustainability indicators. This information includes the environmental impact of their operations, resource usage, and efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, among other things.
Business Model and Policies
The CSRD requires plastics manufacturers to report their business models, including how sustainability considerations are integrated into their strategies. Companies must indicate their policies and processes related to environmental protection, social responsibility, human rights, and anti-corruption measures.
This transparency is implemented to offer stakeholders a comprehensive understanding of how manufacturers approach sustainability across their operations.
Risk Assessment and Due Diligence
A significant difference to the previous reporting framework is that the CSRD explicitly requires companies, including plastics manufacturers, to conduct and disclose risk assessments and due diligence processes related to environmental and social matters.
This involves identifying and addressing potential adverse impacts on human rights, the environment, and society. Manufacturers must demonstrate a proactive commitment to identifying, preventing, and mitigating sustainability risks associated with their operations.
External Assurance Mandate
The CSRD requires a mandatory external assurance requirement for certain sustainability disclosures to increase the credibility and reliability of reported sustainability information. Plastics manufacturers will need to use external assurance providers to verify the accuracy and completeness of their reported sustainability information.
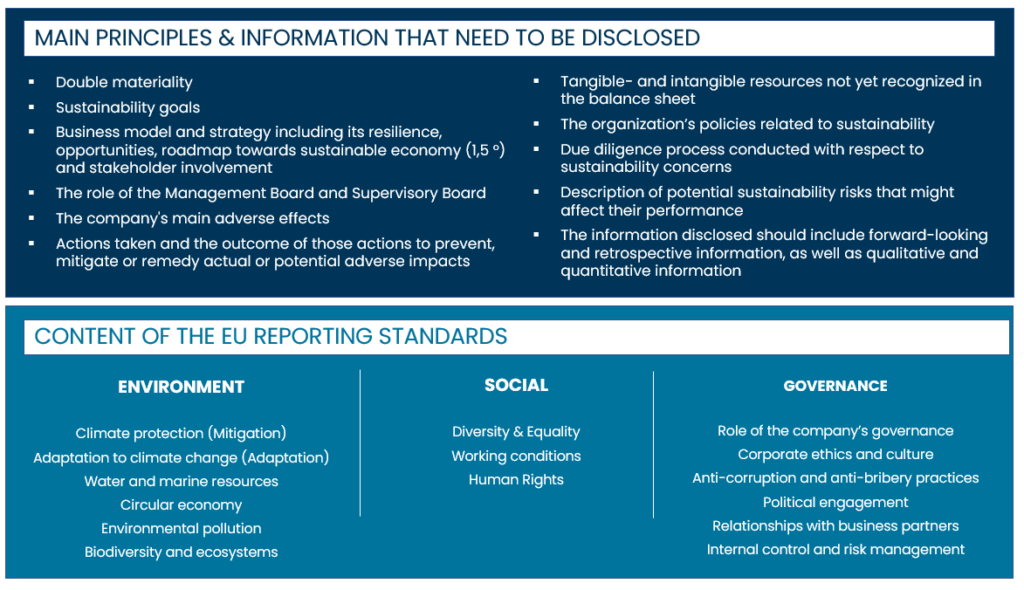
Benefits and Challenges for Plastics Manufacturers
Plastics manufacturers stand to experience both challenges and opportunities amidst the CSRD. This section explores the potential benefits of enhanced sustainability practices and the challenges that manufacturers must navigate towards a more transparent and accountable future.
Benefits
In embracing the CSRD reporting requirement, plastics manufacturers will be regarded as responsible corporate citizens committed to sustainability. Transparent reporting fosters trust among stakeholders such as consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies, which improves the company’s reputation.
Furthermore, investors increasingly consider environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their decision-making. Complying with CSRD meets investor expectations for transparency and can open doors to a broader range of funding options and investment opportunities for plastics manufacturers.
Plastics manufacturers can proactively identify and address potential sustainability risks by conducting thorough risk assessments and due diligence. This aligns with CSRD compliance and strengthens the company’s ability to navigate and mitigate risks, contributing to long-term resilience.
Challenges
The detailed reporting requirements of the CSRD may pose challenges for plastics manufacturers in collecting, managing, and reporting the necessary data. Companies need robust systems to streamline these processes and ensure accurate and comprehensive reporting.
Additionally, compliance with the CSRD may lead to a need for increased resource allocation for data collection, external assurance, and the implementation of sustainable practices. Plastics manufacturers must weigh the potential benefits against the associated costs to maintain a balanced, sustainable approach to compliance.
Moreover, mandatory external assurance adds complexity in adhering to the CSRD. Plastics manufacturers must collaborate with external assurance providers, prompting them to navigate new processes and build relationships with third-party organizations.
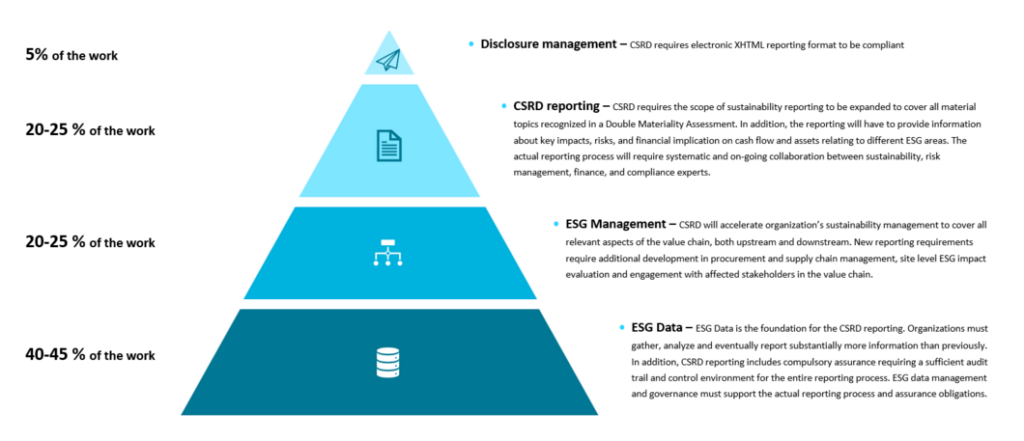
How Can Plastics Manufacturers Navigate the Changes?
In this section, we offer actionable insights to guide plastics manufacturers through the changes brought on by the CSRD, empowering them to comply and thrive in an environment characterized by sustainability, transparency, and responsible business practices.
Integrating Sustainability into Business Strategies
Aligning business models, policies, and operations with sustainability goals can help manufacturers proactively adhere to the CSRD requirements.
Investing in Robust Data Management Systems
By implementing data management systems, plastics manufacturers can streamline the collection, analysis, and reporting of sustainability data. Investing in this technology can enhance efficiency and accuracy while complying with the CSRD.
Collaboration
Collaboration with industry peers and participating in sustainability networks can help plastics manufacturers leverage valuable insights and navigate the challenges posed by the CSRD.
Effective Engagement with Stakeholders
Engaging in meaningful exchanges with stakeholders regarding sustainability efforts and concerns can build trust in a plastics manufacturer’s commitment to responsible business practices.
Real-Time Process Optimization and Digital Threads
On a process level, data-driven, real-time technologies like sensXPERT Digital Mold can help plastics manufacturers maintain a digital thread on each part produced. Integrating real-time process tracking and optimization technologies such as this enhances operational efficiency and seamlessly aligns with the transparency demands of the CSRD.
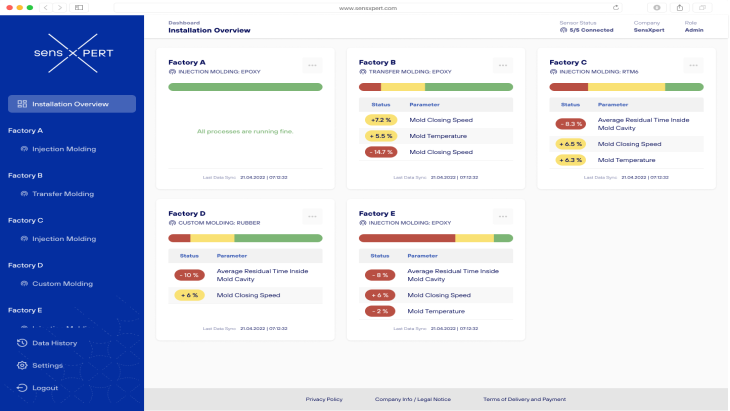
In using Digital Mold, plastics manufacturers gain a solution that provides a comprehensive and traceable record of the environmental impact associated with plastic part processing. Tracking and optimizing processes in real-time empowers manufacturers to make informed sustainability decisions, reduce resource consumption, and contribute to a more transparent and accountable industry.
Learn more about sensXPERT Digital Mold here: sensXPERT’s Plastic Molding Technology