Inefficient Processes & Supply Chain Disruptions: 2024 Solutions
In 2023, Siemens released a report that presents ‘The True Cost of Downtime 2022’. According to the report, Fortune Global 500 companies are now losing a staggering 11% of their yearly turnover, or nearly $1.5 trillion, due to unplanned downtime. This figure paints a concerning picture for the plastics industry, where efficient production is paramount.

Machine or production downtime is just one of the manifestations of inefficient processes, others being ineffective material management, and a shortage of skilled labor. These factors create bottlenecks and hinder production flow. At the same time, disruptions within the supply chain further exacerbate these issues. Shortages in raw materials, transportation delays, and logistical hurdles significantly impact the availability of critical resources and impede overall production schedules.
Understanding the interplay between inefficient processes and supply chain disruptions is crucial for navigating the current landscape of plastics manufacturing. That said, this article explores these challenges, analyzes their impact on production, and explores potential solutions for ensuring a more robust and efficient future for the industry.
Inefficient Processes: Bottlenecks and Lost Production Time
The efficiency of a production line directly translates to a manufacturer’s bottom line. In plastics manufacturing, even minor inefficiencies can lead to significant losses. This section tackles the various process inefficiencies that plague the industry, starting with a hidden time drain: troubleshooting part defects and scrap.
Diagnosing Defects: The Hidden Cost of Downtime
While equipment breakdowns or malfunctions are a well-known cause of downtime, locating the origin for part defects and scrap can be a more inconspicuous time drain. Unlike machine failures, defect-related downtime might not be readily apparent. However, the cumulative effect of these pauses in production can be substantial.
Identifying the root cause of part defects can be a complex process. It often involves analyzing the produced scrap, reviewing machine settings, and potentially even adjusting material formulations. This investigative work requires skilled personnel and can take significant time, leading to production delays.
Additionally, even short interruptions for defect diagnosis can disrupt the flow of production. Molds may need to be cleaned, settings adjusted, and test runs conducted before normal production resumes. These seemingly minor interruptions can add up significantly, impacting overall production output.
Material Management Issues
Besides troubleshooting part defects, material management is another factor that can impact production efficiency. Plastics manufacturers can find it challenging to optimize their material usage and attain consistency in product quality.
One reason for this challenge is the tendency for material overuse in production. The inefficient use of raw materials can bring on significant waste. This can be caused by factors such as improper mixing ratios, inaccurate molding processes, or spills during handling.
Another material management challenge is inconsistent raw material quality. Fluctuations in the quality of raw materials, such as resins and additives, can cause inconsistencies in the final product. This can necessitate adjustments to production processes or even result in part defects, triggering the downtime issues discussed earlier.
The challenges of material management have a direct impact on production efficiency and profitability. Variations in material quality can trigger production delays and rework. Material overuse increases costs and leads to excess waste. In the next section, we will explore another major contributor to inefficient processes – the shortage of skilled labor within the plastics manufacturing industry.
A Growing Bottleneck: Skilled Workforce Shortage
The complexities of modern plastics manufacturing require a skilled workforce with a deep understanding of machinery, materials, and production processes. However, the industry faces a growing challenge: a shortage of skilled labor. This lack of expertise creates bottlenecks and inefficiencies throughout the production line.
For one, modern plastics processing equipment is elaborate and requires skilled operators to ensure efficient and safe operation. A shortage of qualified personnel can contribute to improper machine settings, increased wear and tear, and ultimately, more frequent breakdowns.
Additionally, skilled quality control technicians are needed to inspect raw materials, finished products, and identify potential defects. A lack of qualified personnel in this area can lead to overlooked defects and product quality inconsistencies.
Moreover, the plastics industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies like automation and predictive algorithms playing an increasingly important role. A skilled workforce with the ability to adapt to and leverage these advancements is crucial for staying competitive. The lack of qualified personnel who possess these skills can hinder the industry’s ability of innovative and improve efficiency.
By addressing process inefficiencies like downtime, material management issues, and the lack of skilled labor, plastics manufacturers can ensure a more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable future for their operations.
In the following section, we will explore the challenges of supply chain disruptions, another major factor impacting production efficiency.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The pursuit of efficiency in plastics manufacturing does not solely hinge on internal processes. External factors can also significantly disrupt production. This section explores the problems posed by supply chain disruptions.
Traditionally, a streamlined supply chain ensures a steady flow of raw materials and the timely delivery of finished goods. However, recent years have witnessed a surge in disruptions partly on account of the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical instabilities, creating a more turbulent environment for manufacturers.
These disruptions can manifest in two ways: raw material shortages and transportation delays and logistics issues.
Raw Material Shortages
The plastics industry relies on a steady supply of various raw materials, such as resins, additives, and fillers. However, recent years have seen disruptions in the availability of these critical materials. Geopolitical instability, resource depletions, and unexpected events like natural disasters or pandemics can all contribute to raw material shortages.
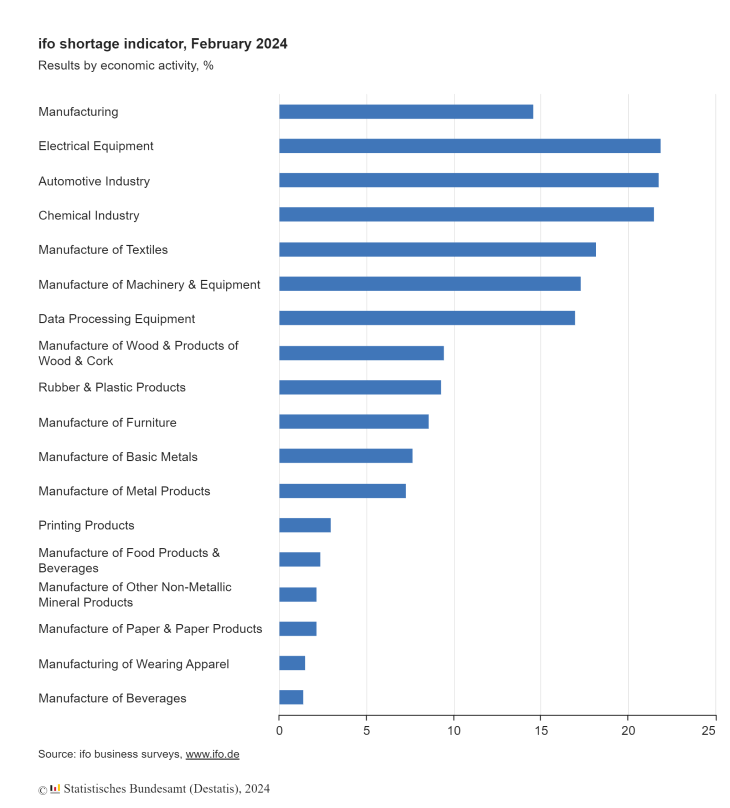
For instance, material shortages have risen in Germany with 9.3% of companies in the rubber and plastic products sector reporting shortages in February 2024. More broadly, 14.6% of companies in the manufacturing sector reported material shortages.
Additionally, Capterra conducted a ‘2023 Manufacturers’ Resource Management Survey’ which found that a significant portion (80%) of small and mid-sized manufacturers report moderate to high concern about getting the raw materials they need over the next year. Plastics, oil, and plant-based materials are in the tightest supply.
The consequences of such shortages are far-reaching.
Production Delays and Missed Deadlines: When essential raw materials are unavailable, production lines can grind to a halt. This results in delays with fulfilling orders and potentially missing- deadlines, impacting customer satisfaction and business relationships.
Price Fluctuations and Increased Costs: Disruptions in the supply chain often lead to price hikes for raw materials. Plastics manufacturers are then faced with the challenge of absorbing these increased costs or passing them on to customers, potentially impacting competitiveness.

Transportation Delays and Logistics Issues
Even when raw materials are readily available, their timely delivery is crucial for efficient production. However, the global logistics landscape faces numerous challenges, playing a role in transportation delays and disrupting the smooth flow of materials.
Such challenges include:
- Congestion at Ports and Shipping Delays – Increased global trade volumes can trigger congestion at ports, causing delays in the shipment of raw materials. Furthermore, factors like labor shortages and unpredictable weather can exacerbate these delays.
- Rising Fuel Costs and Transportation Expenses – Fluctuations in fuel prices can significantly impact transportation costs. This can put pressure on profit margins for plastics manufacturers and potentially hinder their ability to secure reliable transportation options.
The combined effects of raw material shortages and transportation delays can greatly disrupt production schedules, increase costs, and create uncertainty within the plastics manufacturing industry.
Investigating Industry 4.0 Technologies
The challenges posed by process inefficiencies and supply chain disruptions demand innovative solutions. Industry 4.0 is a new wave of industrial automation and data-driven technologies that offers a potential path towards a more efficient and resilient future for plastics manufacturing.
Industry 4.0 represents a paradigm shift towards smart manufacturing. By leveraging data analytics, automation, and digital connectivity, plastics manufacturers can gain greater control over their processes and build a more robust supply chain. Here, we will explore two key areas where Industry 4.0 technologies offer significant potential.
Automation and Smart Technologies: Optimizing Processes and Empowering Workers
Automation has long played a role in plastics manufacturing, but Industry 4.0 takes it a step further with the integration of advanced technologies like:
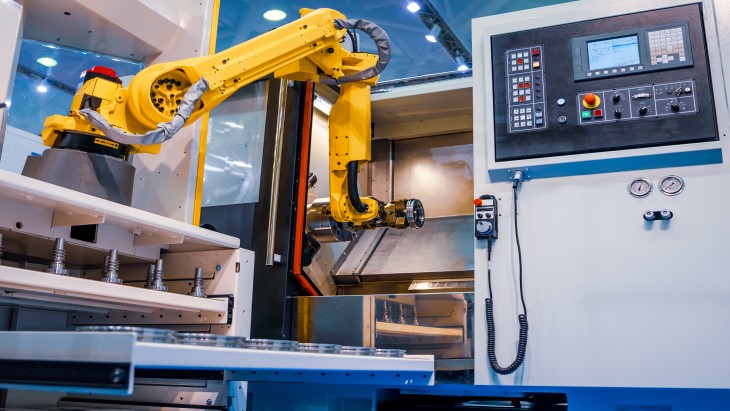
Industrial Robotics – Robots can automate repetitive tasks such as material handling, machine loading/unloading, and quality control inspections.

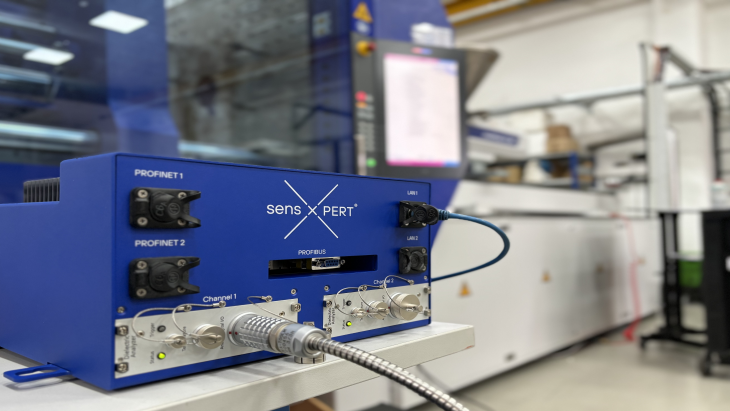
Real-Time Process Monitoring and Predictive Algorithms – Sensor-enabled machines and advanced analytics can provide real-time insights into production processes. This allows for early detection and enables adaptive process control, minimizing unplanned downtime and optimzing process outcomes.

These technologies not only improve efficiency but also empower the workforce. By automating mundane tasks, Industry 4.0 allows workers to focus on higher-level activities like process improvement, optimization, and data analysis.
Building a Connected Supply Chain: Collaboration and Visibility
Industry 4.0 technologies also pave the way for a more connected and transparent supply chain. By fostering collaboration and information sharing with suppliers and logistics partners, plastics manufacturers can gain greater visibility into the flow of materials and proactively address potential disruptions.
Cloud-based supply chain platforms can facilitate communication and data exchange between all stakeholders within the supply chain. This increased transparency allows for better forecasting, proactive inventory management, and a faster response to disruptions.
At the same time, closer collaboration with raw material suppliers and logistics providers can also enable more accurate forecasting and planning. This helps to mitigate the risk of shortages and ensures a steady flow of materials to meet production demands.
By embracing Industry 4.0 technologies and fostering a collaborative approach with the supply chain, the plastics manufacturing industry can navigate the challenges of inefficiencies and disruptions, charting a course towards a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient future.